|
THE NOBEL PRIZE
In your redemptive quest use our A - Z or steer a righteous course HOME toward enlightenment praise the Lord
|
|
|
|
|
Almost any human cell can be used to replicate a person via cloning, but care should be taken when matching DNA to an egg.
BIOLOGICAL REPLICATION
The replication of biological organisms, has been proven to work very effectively. This is commonly called cloning. In science fiction artificial humans are called replicants, cyborgs, or skin jobs, as distinct from synthetic humans, that are actually robots, or organic machines designed to look and act like humans.
Robotic science has not developed this far as yet when it comes to humanoid form. But cloning technology is a fact of life. Though illegal at the present time in many countries. Driving much of the research underground.
In order to be able to duplicate a subject, their DNA is needed. If the DNA is is good condition, i.e., the Genome is complete, replication is a relatively simple matter in the right laboratory conditions.
With the possible exception of identical twins, each person's DNA is unique. This is why people can be identified using DNA fingerprinting. DNA can be cut up and separated, which can form a 'bar code' that is different from one person to the next.
In the future, people might be reincarnated, using technology that exists today that is illegal, in a time when populations are threatened, or other reasons for making such resurrection from storage useful - or legal.
It would then be possible to live forever, a kind of afterlife, dreamed of by Ancient Egyptians, Christians (going to heaven or hell) and many other religions. For this reason, and such as not to dilute the religious beliefs of Catholics and other religions based on Jesus Christ, and the Lord Almighty, the Church are very interested in keeping the whereabouts of Cleopatra a secret.
Today, wealthy people store their bodies cryogenically for many reasons. Sperm and Eggs are also stored cryogenically. Most of the clients of such services, tend to overlook, or otherwise interpret their religious beliefs differently.
In fiction, John Storm is an amateur anthropologist who has amassed a huge collection of Human and other DNA, so creating a digital Ark, where it would be possible to re-create the life of earth, on other planets with suitable atmospheric and other life support.
CLONING TECHNIQUE
Cloning is a technique scientists use to make exact genetic copies of living things. Genes, cells, tissues, and even whole animals can all be cloned.
Somatic cells, on the other hand, already contain two full sets of chromosomes. To make a clone, scientists transfer the DNA from an animal’s somatic cell into an egg cell that has had its nucleus and DNA removed. The egg develops into an embryo that contains the same genes as the cell donor. Then the embryo is implanted into an adult female’s uterus to grow. Unless, you have one of Franco Francisco's artificial wombs.
One can imagine the outcry by women's rights campaigners, imagining themselves as redundant mothers. On the other hand, career women who cannot take time off to have a child, might like the idea. Don't worry ladies, nothing can replace the love and care of a real mother, whether adopting, or giving birth to your own family members.
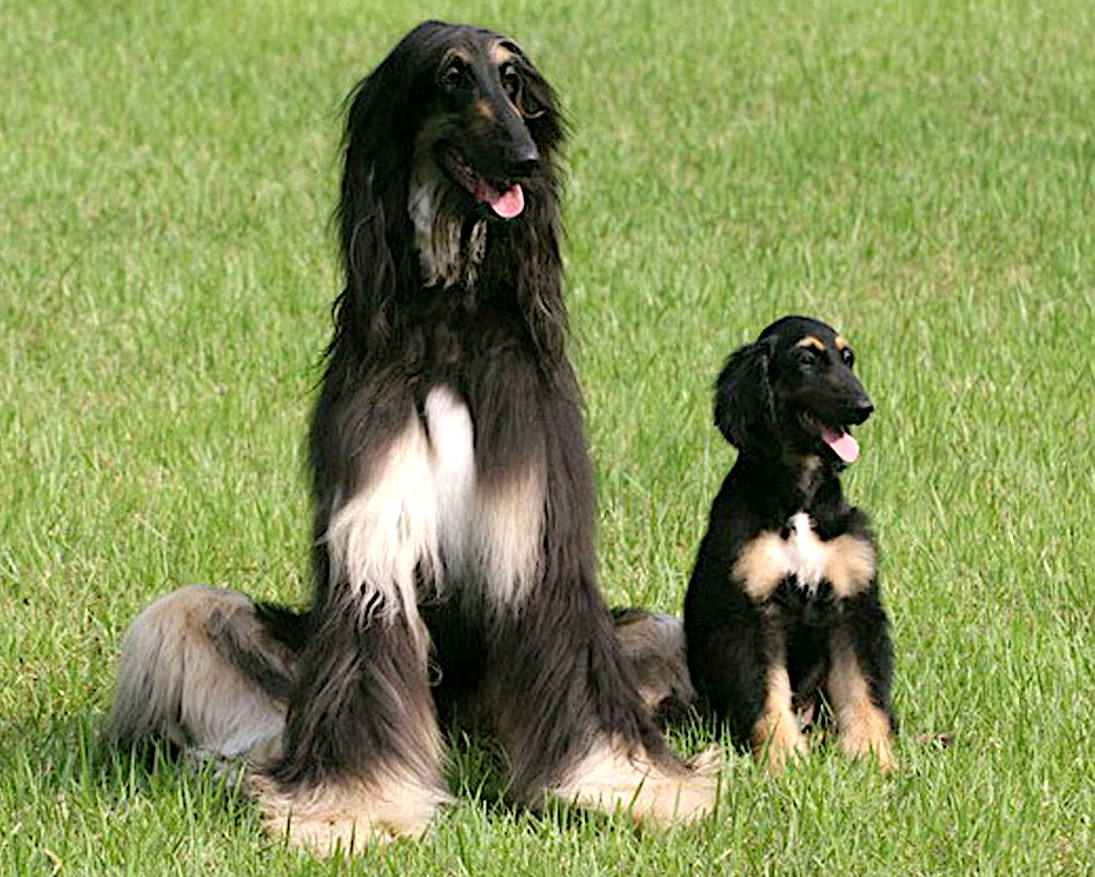
If you are going to clone a human, you might as well copy someone exceptional. This is a picture of Snuppy, the Afghan hound who was successfully cloned to produce three healthy pups.
DOLLY
In 1996, Scottish scientists cloned the first animal, a sheep they named Dolly. She was cloned using an udder cell taken from an adult sheep. Since then, scientists have cloned cows, cats, deer, horses, and rabbits. They still have not cloned a human, though. In part, this is because it is difficult to produce a viable clone. In each attempt, there can be genetic mistakes that prevent the clone from surviving. It took scientists 276 attempts to get Dolly right. There are also ethical concerns about cloning a human being.
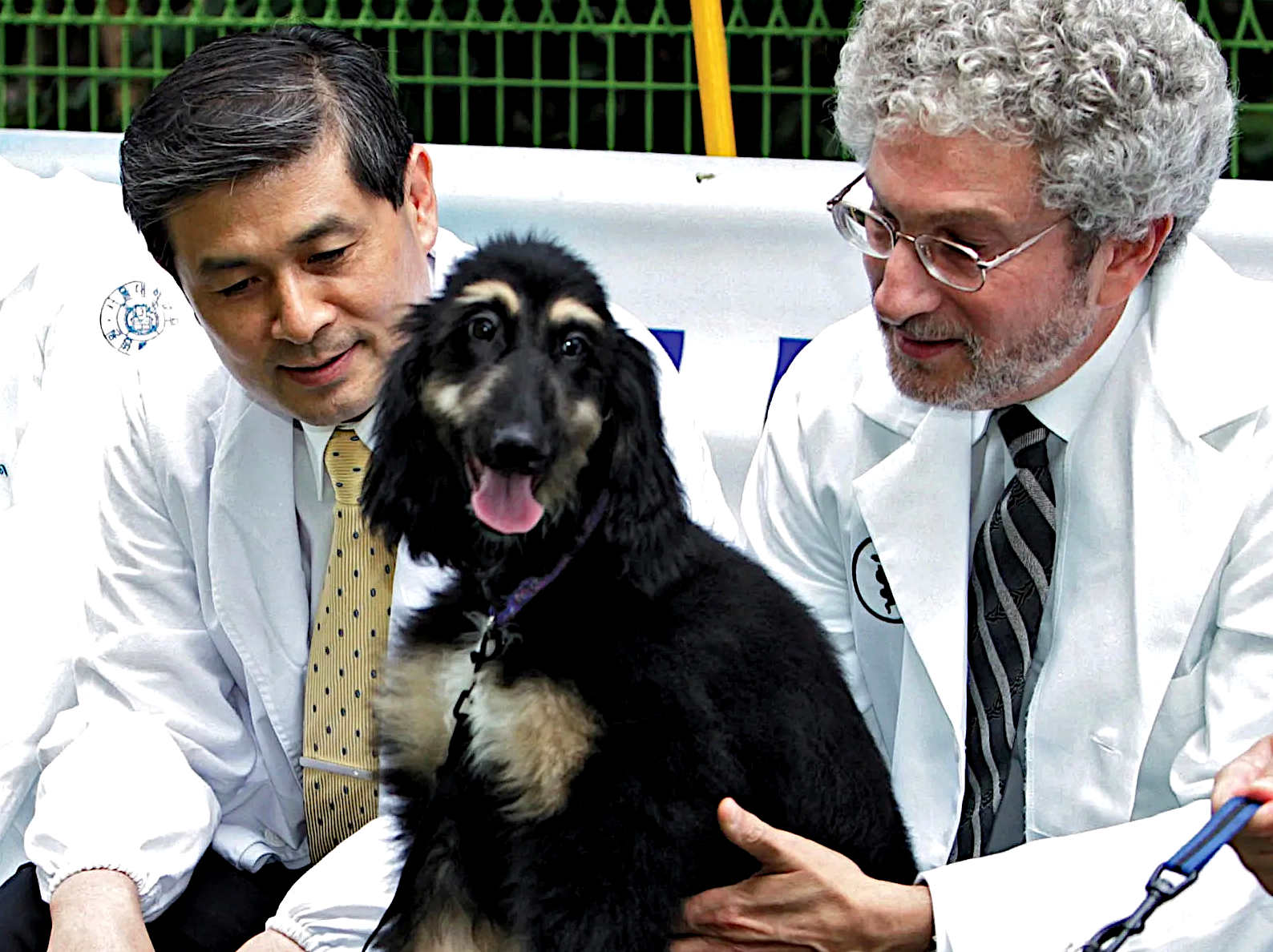
APRIL 2005 - Snuppy, the first successfully cloned Afghan hound, sits with his generic father at the Seoul National University on August 3, 2005 in Seoul, South Korea. The dog joined the list of cloned animals as South Korean scientists, led by stem cell researcher Dr. Hwang Woo-Suk, announced that they have created the first cloned dog from an Afghan hound in the world.
SNUPPY
In April 2005, a dog named Snuppy was successfully cloned by Korean scientists. The male Afghan Hound named Snuppy, was born on April 24; scientists created him using a cell from the ear of an adult Afghan Hound and the procedure involved 123 surrogate mothers, of which only three produced pups and of the three puppies only Snuppy survived.
HUMAN CLONES
Human cloning is inevitable. It has already taken place conceptually.
We are not talking about the “artificial twinning” experiments performed in 1993 at the Washington University Medical Center. Although newspapers were quick to trumpet this as human cloning, it was soon revealed that in reality this was a relatively primitive procedure in which an already-fertilized egg was split into two fertilized eggs. A nice party trick, but Mother Nature already does it thousand of times a day when she creates twins, triplets, etc. Further proof that the concept of cloning is sound.
The real cloning took place two years later, in 1995, although it wasn’t revealed until mid-November 1998. Unbelievably, only a few small newspaper stories weakly revealed one of the most important biotechnology developments of all time. In fact, it’s probably one of the most important developments in the history of science and technology.
Working under the auspices of the private company Advanced Cell Technology, and using the facilities of the University of Massachusetts at Amherst, scientists James Robl and Jose Cibelli created a human clone. They took cells from Cibelli’s leg and cheek, put them alongside a cow’s ovum with the genetic material stripped out, and added a jolt of electricity.
One of Cibelli’s cells fused with the cow’s ovum, which acted as though it had been fertilized, and the cells began dividing. This is the same process used to create Dolly, the cloned sheep from Scotland, only this was done before Dolly was created.
A small story in the Boston Globe reported the following about this achievement:
Mitochondria are power generators in the cytoplasm of the cell. They grow and divide inside cells and are passed on from one generation to another. They are present in sperm and eggs.
Judging by the successful growth of the combined human-cow clone creation, it appears that cow mitochondria may well be compatible with human embryonic development.
NEW SCIENTIST 26 DECEMBER 2002
The world’s first cloned baby was born on 26 December, claims the Bahamas-based cloning company Clonaid. But there has been no independent confirmation of the claim.
DO CLONED HUMANS THINK THE SAME AS THE ORIGINAL?
The simple fact of replicating the biological host of a human, does not re-create the person providing the DNA. For that to happen, additional technology is needed. This is the technology that Baron Heinrich Richthofen and his team are developing, in the quest to fuse royal Egyptian and Aryan blood, to produce a queen that thinks like Cleopatra, from which sons and daughters may flow.
In the Hollywood movie: The Boys From Brazil, Neo-Nazis attempt to clone Adolf Hitler, and provide the replicants with a similar up-bringing, in the hope the duplicated human boys will grow up to be like the German dictator.
From our point of view, though the concept might work given an infinite number of variables and unlimited time, there is a more positive method of re-creating an exact copy of a subject's brain. Which would otherwise develop according to the environment it encounters when maturing, from the time it is brought back to life. The Frankenstein films focus on this aspect, when the Baron Victor, uses a damaged brain, leading to unstable results - fiction though it may be, they had a point.
Pets that are cloned would not recognize their masters, they would have to be re-trained. It would not matter for other animals, such as dinosaurs, except that they would be biologically programmed for life in the Jurassic period. Hence, might not survive, or might be more prolific, such as might be the case with seven billion humans as a vast food resource. Anyone would have to be nuts to even consider cloning dinosaurs, like the fictional Dr. John Hammond. All the franchised 'Jurassic' films tell us the same thing. Don't do it! Far less dangerous is the cloning of his supposed granddaughter, Maisie - from his deceased daughter - by Sir Benjamin Lockwood, in the 2018 film Jurassic World - Fallen Kingdom. All fiction of course. But, entertaining fiction, based on cloning.
The cloning method Baron Richthofen and his team prefer, stands a very good chance of success - and is far more sane than replicating dinosaurs. If the plan to clone a long- lost Pharaoh can ever be viewed as anything but research far removed from a sound scientific experiment. For most of us. Ignoring for now theology and mythology.
But
who can understand the workings of an obsessed mind. Provided
the Baron's team can find the near
intact DNA of an Egyptian pharaoh, as the starting point, he
is intent on giving it a go. Only John Storm and the crew of
the Elizabeth
Swann, might prevent something unholy taking
place. In a world besieged by corruption and aggressive
inhumanity to our fellow man, does it matter? John Storm
believes in the natural world, and not
interfering with nature, unless absolutely unavoidable.
Exceptions being for the
advancement of medicines to cure (at present) incurable
diseases. Or, for
the alleviation of suffering.
REFERENCE
https://www.
|
|
|
In your redemptive quest use our A - Z or steer a righteous course HOME toward enlightenment praise the Lord
This website is Copyright © 2023 Cleaner Ocean Foundation & Jameson Hunter
|